Modern banks handle a multitude of financial transactions involving significant money flows and enormous volumes. Consequently, banks have become prime targets for fraudulent activities. In 2023, an impressive $10 billion loss was attributed to fraud, with nearly 1 in 5 people affected by imposter scams.
The challenge for banks is that modern criminals are highly tech-savvy, leveraging the latest technologies to access user data and money. Financial organizations must therefore adopt advanced methods to prevent banking fraud.
This comprehensive guide delves into the methods of preventing bank fraud, the role of IT technologies in fraud prevention, and how financial institutions work with high-risk customers. Based on extensive expertise in this field, we will explore the most advanced methods of bank fraud protection.
What Is Banking Fraud?
Banking fraud refers to activities that result in unauthorized money being obtained through deceptive means.
Examples of Banking Fraud
Banks use various methods to protect against fraud, involving both customer screening and transaction monitoring.
Customer Screening
Pros:
Cons:
Example: Using the Dow Jones list, customer data such as name, surname, family members, passport information, and employment details are checked against sanctioned individuals. The system generates alerts for data matches, which are then investigated further.
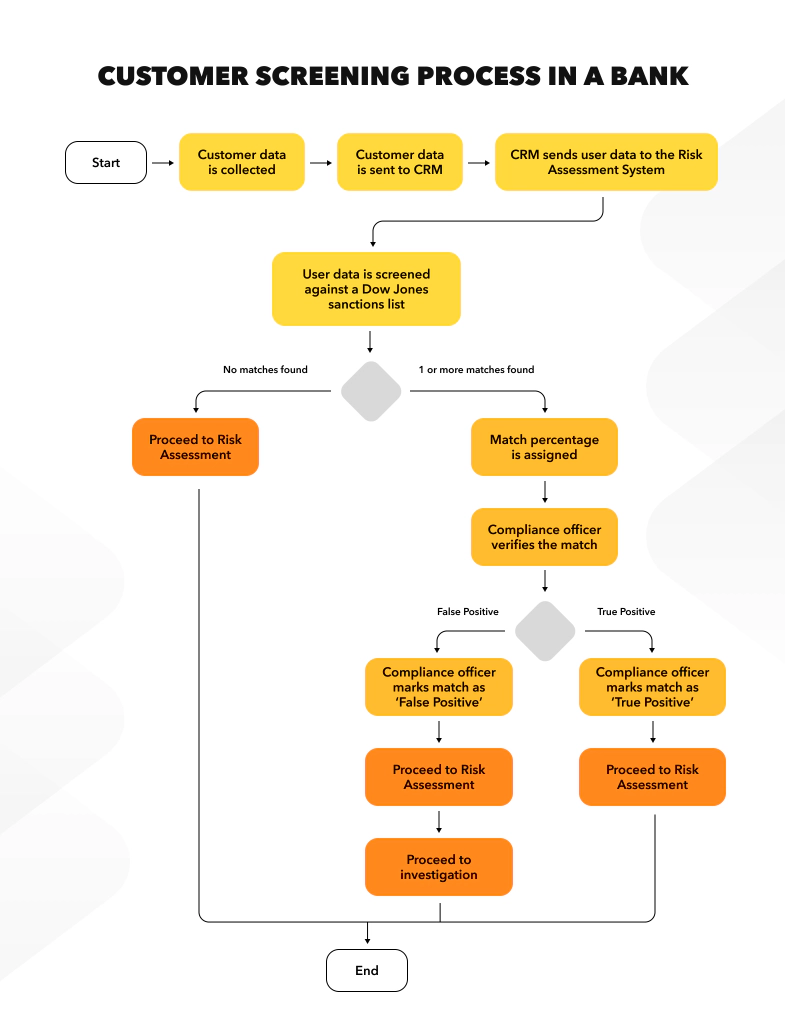
Pros:
Cons:
Most effective with robust data architecture and sufficient data.
Example: A fraud management system analyzes customer behavior patterns. For instance, a customer with a $5000 monthly income and typical expenses suddenly makes unusual payments to new accounts. The system flags and blocks these transactions for further verification, preventing potential fraud.
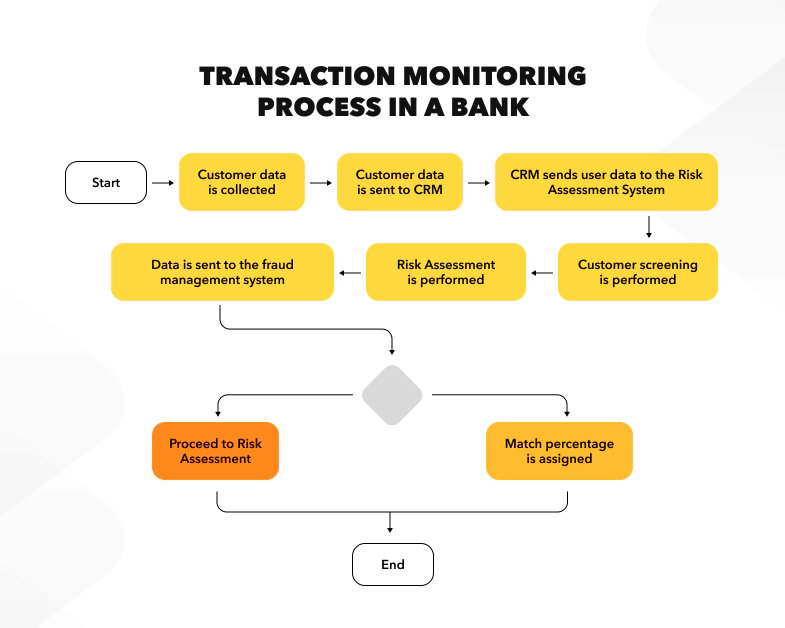
Banks conduct various fraud prevention checks at different stages of customer interaction:
Customer Onboarding Check
Monetary Transaction Check
Non-Monetary Activity Check
Overnight Check
Every night, banks perform fraud protection procedures for all existing customers, ensuring regular updates and accurate risk categorization.

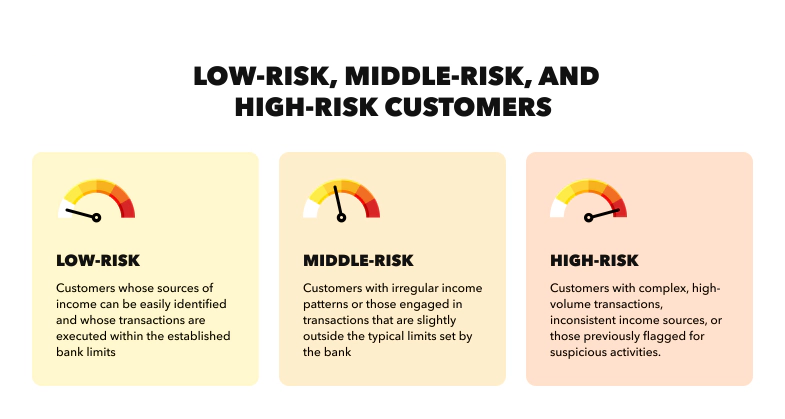
Banks categorize customers into low, middle, and high-risk categories, applying specific measures for each to ensure data safety and prevent fraudulent activities.
1.Low-Risk Customers
Typical Representatives:
Fraud Prevention:
2.Middle-Risk Customers
Typical Representatives:
Fraud Prevention:
3.High-Risk Customers
Typical Representatives:
Fraud Prevention:
If fraud is suspected, banks gather additional details such as proof of income, source of funds, and transaction history. They may require approvals from security officers and management. Depending on the investigation outcome, the bank may proceed with or halt onboarding/dealing with the customer, potentially leading to account closure.
To develop fraud prevention software, you need a team with extensive experience in Fintech development and a comprehensive understanding of the regular basis in this industry.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-based software provides flexibility in fraud management, enabling unbiased evaluation, instant responses to malicious activity, and minimizing errors.
Software Developing effective fraud prevention software requires a team with extensive experience and a comprehensive understanding of the banking industry. At Sprinterra, we possess these skills and invite you to discuss your anti-fraud software project with us.
By leveraging advanced technologies and implementing robust fraud prevention measures, banks can effectively protect themselves and their customers from fraudulent activities.
Get the latest insights on exponential technologies delivered straight to you
© 2025 Sprinterra. All rights reserved.