Before delving into Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for the Financial Services sector, let’s first gain insight into the current landscape. The business arena is in a constant state of flux. Within this dynamic context, the financial industry faces mounting pressure to reduce expenses while simultaneously elevating customer service standards without compromising its competitive advantage.
Today’s customers crave convenient and swift access to services and highly personalized experiences that offer exceptional value for their money. Financial institutions are tasked with meeting these demands while keeping their operational costs in check, and this is precisely where the power of Robotic Process Automation comes into play. RPA entails the deployment of bots that emulate the routine, day-to-day tasks governed by established business rules, tasks that can be easily automated. Consequently, a significant number of financial institutions are increasingly adopting RPA as the means to fulfill these imperatives.
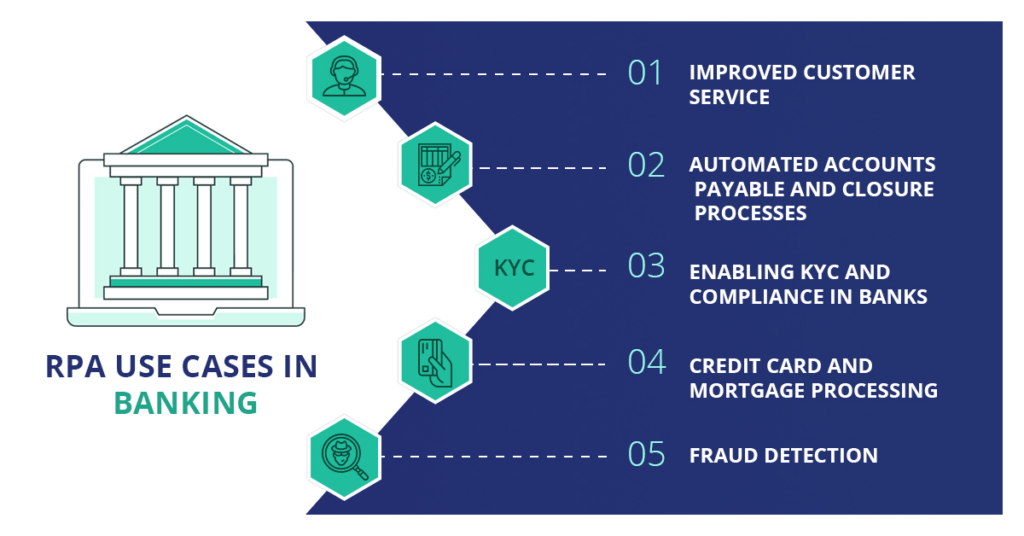
This technology enables financial institutions to offer round-the-clock support for critical activities and processes. With the ability to access real-time assistance, these institutions can deploy their staff more strategically.
Robotic accounting, also called accounting process automation, leverages applications like UiPath and Blue Prism to reduce the human effort required for processing transactions within accounting and finance departments. These “accounting robots” are tools that streamline routine data transfer between accounting systems and external applications rather than confining their capabilities to a single function.
It’s important to clarify that accounting automation isn’t a complete replacement for human involvement but rather functions as a “bionic arm” that enhances the efficiency of finance and accounting professionals by minimizing the manual data handling workload. UiPath, Blue Prism, and Automation Anywhere have simplified the creation of an artificially intelligent accounting workforce, commonly known as RPA bots, by eliminating the need for expertise in programming to facilitate data integration across various sources.
Banks, financial institutions, and insurance companies are prominent adopters of automated processes. In today’s rapidly evolving landscape, these entities are driven by a dual agenda: enhancing customer satisfaction and staying competitive against virtual banking solutions. The relentless pursuit of efficiency improvement and resource optimization has led them to embrace process automation.
Within the banking and financial sector, automation serves two primary functions:
For the finance industry, automation emerges as a pivotal tool to address sector-specific demands and elevate operational efficiency, all while trimming costs through the services-through-software paradigm. A strategic approach is imperative to capitalize on the opportunities within their industry.
Within financial services, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) primarily targets mundane administrative tasks, such as transferring data from emails to the system. It operates at the presentation layer, where it excels at tasks like data extraction from multiple sources, which consume a significant portion of a workday.
Numerous US banks and insurance companies have already integrated RPA into their processes, automating approximately 800 operations. The remarkable growth of RPA is evident when considering that the financial industry is projected to reach a value of $2.9 billion by 2023, a substantial leap from its $250 million valuation in 2016, as reported recently.
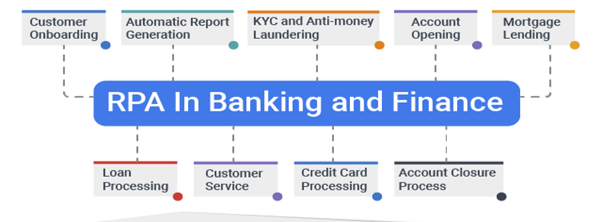
Customer Onboarding:
Customer onboarding is often a protracted and labor-intensive process due to the need for manual document verification. This entire procedure can be streamlined through the use of automation tools. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology can extract data from Know Your Customer (KYC) documents, which can then be cross-referenced with the customer-provided information. The data can be automatically entered into the customer management portal if no discrepancies are found. This eliminates the possibility of errors and conserves time and effort expended by employees.
KYC and Anti-Money Laundering (AML):KYC and AML processes are data-intensive, rendering them well-suited for Robotic Process Automation (RPA). RPA can be applied to detecting suspicious banking transactions and automating manual procedures. Its swift implementation saves time and reduces costs compared to traditional solutions.
Account Opening: The implementation of RPA has streamlined the account opening process, making it more efficient, rapid, and accurate. Automation eradicates errors that may arise between the core banking system and new account opening requests, thus enhancing data quality within the system.
Mortgage Lending: Mortgage lending is a highly time-consuming process, making it an ideal candidate for automation. RPA enables the automation of critical tasks in the mortgage lending journey, including loan initiation, document processing, and quality control. This expedites the process, resulting in heightened customer satisfaction. Additionally, it relieves employees of manual tasks, allowing them to focus on essential responsibilities.
Loan Processing: Loan processing has historically been perceived as an uphill task despite some degree of bank automation. Further automation can reduce the processing time to 10-15 minutes. This transformation would enhance customer satisfaction and alleviate the workload on employees.
Customer Service:The sheer volume of routine customer inquiries challenges staff to respond promptly. Utilizing RPA tools can automate these mundane, rule-based tasks, enabling real-time answers to queries and reducing turnaround times significantly.
Credit Card Processing: involves extensive validation checks, making it complex and tedious. However, implementing an RPA strategy allows for rapid decision-making using a rule-based approach, whether to approve or decline an application.
Account Closure Process: The bank often encounters a substantial volume of monthly account closure requests, primarily due to customer non-compliance. RPA can address this issue by efficiently tracking such customers and automatically generating notifications and reminders for submitting required documents.
A global insurer, Zurich has achieved significant efficiency gains by implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA). This move has liberated up to 40% of their commercial underwriting process, enabling them to redirect their focus towards high-value-added tasks, especially in handling complex policies. Following a successful pilot program that resulted in a remarkable 50% cost reduction, Zurich decided to expand the implementation of RPA, earning them recognition and an award for their efforts.
Another major global insurer operating worldwide with diverse lines of business reaps the benefits of RPA adoption. Previously, they had to navigate through 26 sites and perform multiple searches to ensure timely claims payments. This process needed to be repeated four times on various dates each month. With the introduction of RPA, this once 4-day task has been reduced to a mere 2 hours, saving thousands of hours of Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) work annually and reducing errors.
In the case of the Singaporean bank OCBC, the deployment of RPA has revolutionized the home loan repricing process. What once took 45 minutes to complete now requires only 1 minute. The bot expedites the repricing, verifies customer eligibility, offers repricing options, and even drafts recommendation emails.
As exemplified by Sumitomo Mitsui, Japanese financial institutions have harnessed automation to extraordinary effect. They managed to eliminate a staggering 400,000 hours of manual labor for their employees by automating various processes, signifying a substantial leap in efficiency.
Here is an improved rendition of the provided details:
Every process transformation and introduction of new technology carries inherent risks that can impact an organization’s functionality. However, compared to long-term core technology implementations, the risks associated with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are considerably lower. This is primarily because robots can be deactivated and their effects are confined to individual user desktop settings. Here are a few key risks associated with RPA:
In the realm of financial market automation services, numerous vendors operate, but a select few stand out as leaders. These frontrunners include:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) finds valuable use cases in the field of Finance and Accounting, as illustrated below:
Daily Sales Reconciliation (DSR): In a scenario where a client handles significant volumes of cash and credit card transactions across multiple locations daily, the management team faces the challenge of interpreting these transactions for real-time financial analysis. Manual journal entries are prepared by analyzing Point of Sale (POS) files from various locations. Subsequently, all transactions, including those involving cash, credit cards, and Amex, are reconciled with bank statements to ensure transaction accuracy. Any discrepancies detected require a thorough investigation.
This process is notably time-consuming, especially when transaction volumes are substantial, leading to extended reconciliation times and an increased likelihood of errors. Introducing RPA into this workflow can significantly enhance efficiency. RPA bots can extract transaction amounts, match them with bank statements for each tender type, and promptly flag any discrepancies, thus streamlining the process.
Bank Reconciliation (BRS): Bank reconciliation involves comparing an entity’s financial report balances for cash accounts with the corresponding data on bank statements. The aim is to identify discrepancies and, if necessary, make adjustments to ensure accurate accounting records. Regular bank reconciliations are crucial to ensure that a company’s cash records align with expectations, preventing issues like bounced checks or overdraft fees.
The BRS process typically entails clearing checks in an Oracle system. It begins with identifying common and uncommon checks within files downloaded from Oracle and bank statements, subsequently clearing the common checks present in both data sources. Additionally, the BRS process involves reconciling cash and credit card transactions with data from both Oracle and bank statements, as well as segregating other transactions, such as bank charges, cash pickup fees, exchange gains, and deposits.
BRS, being a repetitive and time-consuming task, can be improved with the introduction of RPA. By leveraging RPA bots, organizations can automate the reconciliation process, allowing employees to collaborate with the bots to achieve more efficient and accurate results, while also enhancing employee satisfaction with the process.
RPA has already garnered a substantial customer base across various industries, particularly businesses seeking cost reduction and heightened efficiency. Its core aim is to optimize human resources by minimizing the efforts required. This technology holds immense potential to revolutionize the landscape of financial services. Moreover, it presents opportunities to expedite business processes through automation, liberating employees from laborious manual tasks.
Through RPA deployment, enterprises can streamline functions such as accounting, proficiently gather and consolidate data, and trim expenses across multiple branches. It also enables the provision of round-the-clock customer support, contributing to an exceptional customer experience while reducing the risk of cyber fraud.
Get the latest insights on exponential technologies delivered straight to you
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site. By using our site, you consent to cookies.
Manage your cookie preferences below:
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Google reCAPTCHA helps protect websites from spam and abuse by verifying user interactions through challenges.
Google Tag Manager simplifies the management of marketing tags on your website without code changes.
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us understand how visitors use our website.
Google Analytics is a powerful tool that tracks and analyzes website traffic for informed marketing decisions.
Service URL: policies.google.com (opens in a new window)
Clarity is a web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic.
Service URL: clarity.microsoft.com (opens in a new window)
Marketing cookies are used to follow visitors to websites. The intention is to show ads that are relevant and engaging to the individual user.
LinkedIn Insight is a web analytics service that tracks and reports website traffic.
Service URL: www.linkedin.com (opens in a new window)
You can find more information in our Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy.